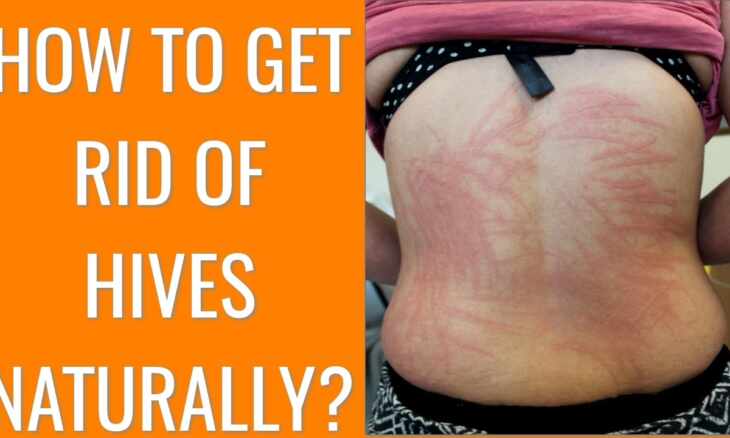
Suffering from hives like itching, invasive red patches, regular or occasional, the symptoms are no less annoying. Here are our answers to how to get rid of hives?
There are various symptoms of hives. Another name of hives is Urticaria.
It results in raised patches that itch badly. The acute urticaria attack, lasting from a few hours to a few days, passes by itself. However, you should call emergency services if you have a fever, swelling of the face, and difficulty breathing. Beyond several weeks, it is a chronic condition, and you should consult a doctor. So let’s know more, how to get rid of hives.
How to get rid of hives?
Solutions to prevent hives attacks
Avoid the factors that can be at the origin of this allergy. Such as drugs, foods, or physical causes (pressure on the skin, heat, or cold).
Cut down on fried or fatty foods, as they complicate digestion and can lead to inflammation.
Choose fruits and vegetables
You have to reduce or eliminate dairy products. Such as cow, goat, sheep usually promote allergies. Cheeses contain histamine, which causes itching.
Limit the consumption of tea, coffee, alcohol, and wine. Like drinks that irritate mast cells (cells that release histamine).
Treat yourself to sauna or hammam sessions. They will help you to remove waste and dead skin cells.
In the event of an attack of urticaria
Apply ice water compresses to the patches. The cold eases the pain. You can also put cotton soaked in apple cider vinegar.
Cleanse your liver, especially if you take medication regularly. 2 times a year, for 20 days, take a cure of milk thistle and desmodium.
Or you can apply artichoke and black radish. Birch sap also gives good results.
Drink nettle tea: 10 g of dried leaves (1 tablespoon per cup). It infused in 75 cl of water for 15 minutes.
Most effective way to get rid of hives
Lavender helps heal skin sores and reduce irritation from hives. Besides, it will numb the pain and calm the itching.
If the signs do not go away, you should consult your doctor. Doctor will prescribe medication. Social Security does not fully cover the latter. You will then need to be reimbursed by your mutual insurance company.
You can use the comparator below to find the mutual.That suits you at the best price.
Urticaria: the information you should know
Hives and itchy skin
There are many causes of itchy skin. They can trigger following an allergy or following an illness such as eczema, for example.
It can also be the consequence of an insect bite or a normal bite.
Since they are a symptom of something, you should not take them lightly. Therefore as soon as the last or are associated with redness. Quickly consult a dermatologist.
Indeed, only a specialist will tell you if it is a banal itching or a real skin condition. It will also determine if an internal disease is in progress.
Most of the time, he will recognize the signs of hives. And prescribe the appropriate treatment.
What is urticaria?
It is an inflammatory reaction of the skin. This rash is common and affects 15 to 20% of the population in the USA.
It’s not a disease, but it can be a symptom. Also it is very bothersome, which can relieved by taking antihistamines.
Seizures last from a few minutes to a few hours. And go away independently without leaving scars.
Yet this benign condition can have a heavy impact on people’s quality of life. Especially, who suffer from it. Itching is indeed painful to live with, particularly when it comes to chronic urticaria.
Symptoms of urticaria
Symptoms vary from person to person. The rash usually shows up as prominent pink or red patches. It is with a sharp border called “erythema” or “papules.”
They also change places and draw circles on the skin. They are fleeting and disappear on their own after a few hours. It happens without leaving any traces.
The plaques look like nettle stings (hence the name). And can be of varying sizes (from a few millimeters to a few centimeters). They usually appear on the arms, legs, and chest.
Erythemas accompanies by “pruritus,” that is to say, itching. These can sometimes be very intense.
In some cases, the patient may experience “angioedema” (swelling) on the face. Also, mucous membranes, extremities, and genitals. It happens when the rashes do not start on the skin’s surface. But rather it comes deep down.
A fever can occur as abdominal or joint pain.
People at risk: how to get rid of hives?
Anyone can have hives. 20% of people have a hives attack at least once in their life. However, some people are at risk of more than others:
- women are more affected than men. Especially those between 30 and 40 years old
- when there is a family history of urticaria
- If there are blood abnormalities. Or a deficiency in certain enzymes;
- in case of a systemic disease. Such as lupus or an autoimmune thyroid.
Diagnostic
The diagnosis is more about the causes of urticaria than the hives themselves. An allergology assessment is necessary in case of suspected allergy. Skin tests and IgE antibody assays must then carry out. They are not needed for chronic urticaria. Because it is not an allergic disease.
On the other hand, as urticaria is often associated with other diseases. In particular autoimmune disease, it will be necessary to do further research. A blood count (a study of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, etc.). Examine the speed of sedimentation, look for inflammation, do a liver test. See if there are markers of autoimmune diseases.
Causes of urticaria
Little known about the factors that trigger urticaria. However, we know that seizures are often due to an allergy. Mast cells – immune cells found in the skin’s outer layers. They are more sensitive when a foreign substance is detected. They activate, release histamine. And thus trigger an inflammatory reaction, the urticaria attack.
Many environmental factors can also worsen. Or trigger attacks of acute urticaria. We distinguish :
Drug urticaria. In 30 to 50% of cases, taking certain medications can cause a flare-up. It can be an antibiotic, an anti-inflammatory, morphine. Any drug can trigger a seizure. And the patient may forget to specify that he or she has taken such a treatment. That seems trivial to him. Such as laxatives, sleeping pills, eye drops, or an IUD. Even toothpaste can cause a seizure e.Food urticaria. Some foods, if eaten in too much, can trigger hives. It’s about :
- Urticaria caused by pneumallergens. Pollen, dust, animal hair are also responsible for allergy, asthma, or rhinitis. And these can lead to hives.
- Contact urticaria . Many substances can be responsible. Such as plant, an animal, a textile, cosmetics. Or industrial products such as ammonia.
- Exposure to heat (including the sun) and cold, insect bite, emotional stress can also trigger. Just like pregnancy in women or underlying disease. Such as kidney failure, thyroid problems, or a liver problem.
You should note that these various factors can also lead to chronic urticaria. However, in 70% of cases, no cause is found. So we speak of idiopathic urticaria.
The different types of urticaria
There are two types of urticaria: acute urticaria and chronic urticaria.
Acute urticaria causes attacks (flare-ups) that last from a few minutes to a few days. If the flare-ups last more than 6 weeks and occur every day. Or every 2 to 3 days, this is called chronic urticaria. This urticaria only affects 1 to 5% of the population. And it can last for years. It subsides spontaneously.
Recurrent urticaria is characterized by recurrent attacks. But not continuous.
Urticaria is called “giant” when it affects a large area of the skin.
Treatments for urticaria
When we know the origin of urticaria, recovery is not far away. It is then sufficient to avoid contact with the agent who triggers it. On the other hand, when the causes are unknown. The doctor will prescribe symptomatic treatments.
Antihistamines
To treat urticaria, the doctor prescribes anti-H1 antihistamines like Atarax, Primalan, or Zyrtec. They are 90% effective and act quickly (within half an hour or hour of the attack onset). Be careful, however, as they can cause drowsiness.
When the urticaria persists (more than 6 weeks). The doctor may increase the doses or change the treatment.
If antihistamines do not work, he will prescribe:
- an immunosuppressant (of the cyclosporin type);
- antileukotrienes
- a monoclonal antibody against IgE (omalizumab);
- tranquilizers and anxiolytics.
In case of angioedema, the patient will inject cortisone. It will reduce the inflammation. In very severe cases (when the patient cannot breathe). Intubation may be necessary and a tracheotomy considered.
Anaphylactic shock treatment will be the injection of an adrenaline shot. A pen injector most often to prick on the thigh.
Medicines in local application
They are generally of little use in the context of urticaria. And then, it causes photosensitization. And allergic contact eczema. However, some topical creams can relieve itchy skin like ‘Eurax’.
This cream contains crotamiton, an active agent that soothes itching in patients with dermatitis, eczema. Or it will following an insect bite. You can apply it during a hives attack (2 to 3 times a day).
Anti-itch tips of how to get rid of hives
The first instinct is to scratch yourself. However, do not scratch. As this can lead to a risk of infection. The skin is exposed and therefore exposed to germs.
However, you will need to protect your skin from dryness with mild, moisturizing cleansers. Opt for nourishing products that will repair the skin barrier. And therefore soothe it. Take them without preservatives, dye and soap. Uriage or Bioderma treatments are very useful.
And above all, as your skin must always be hydrated. Avoid irritating it by wearing tight clothes. Or textiles that itch (wool, and nylon in particular).
FAQ of how to get rid of hives?
FAQ of how to get rid of hives?
1. What foods should you avoid during hives?
Food urticaria
Foods rich in histamine: fermented drinks (beer, etc.). Also fermented cheeses (Roquefort, Brie), fish, sauerkraut, canned food, tomatoes, etc. Foods rich in tyramine: cheeses, smoked fish, sausages, pheasant game. Also, tomatoes, cabbage, grapes, white wines, etc.
2. How To Treat Grandma’s Urticaria Remedy?
To relieve the itching, especially in little ones who have trouble not scratching. Fill a bowl with lukewarm water. Add half a glass of cornstarch and half a glass of baking soda. Then make soak limbs affected by Urticaria. It usually calms the itching quite well.
3. Is Urticaria dangerous?
Isolated hives are not usually life-threatening. But they can be extremely unpleasant.
It is essential to remain calm. And, if your doctor has already prescribed it, start an antihistamine (antiallergic) treatment. It can help you to reduce the symptoms.
4. How to calm itching?
Our advice to calm the itching:
Use a cold compress and rinse your eyes with water before taking an ophthalmic treatment. Apply a moisturizer and care products suitable for your skin. Or you can use mild and natural soaps. And you should avoid chemical detergents for your laundry.
5. What can cause hives?
We speak of a giant or generalized Urticaria. When the plaques are spread over several parts of the body and come together. It can be caused by food (peanuts, shellfish, cheese). Dust, a chemical, an insect bite, a drug, or stress.
Conclusion of how to get rid of hives?
Some forms of urticaria affect the lives of patients. Especially chronic urticaria. It causes stress and insomnia. The sufferer is often frustrated. When they cannot find the right treatment quickly.
Also, some hives can cause swelling (edema) on the skin. These lesions that appear on the face, hands, or feet are very painful. Rare cases of edema in the throat may occur. The patient’s vital prognosis is then engaged. Because it is difficult for him to breathe.

